Foot care represents a significant aspect of health management for people living with type 2 diabetes. This condition may lead to unique challenges that require careful attention to prevent complications. Recognizing how diabetes affects foot health and understanding diabetic foot care can help reduce risks and improve overall well-being.
How Does Type 2 Diabetes Affect Foot Health?
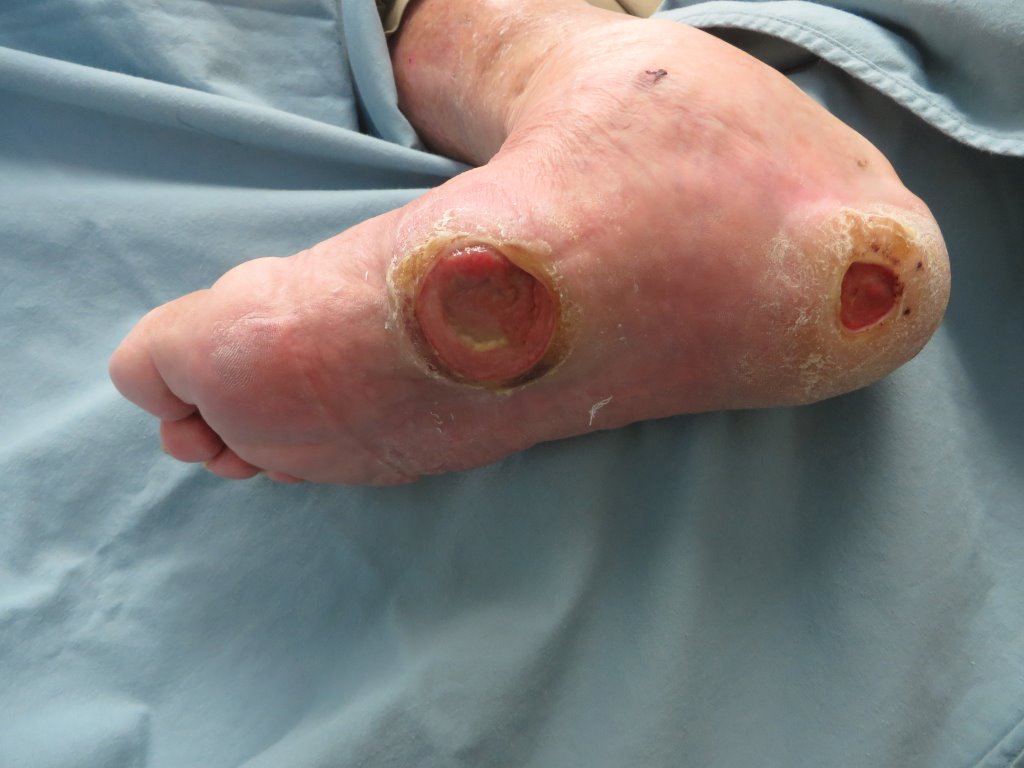
Type 2 diabetes has the potential to affect foot health in several ways due to persistent high blood sugar levels. Elevated blood glucose levels can impact nerves and blood vessels, which are fundamental for maintaining healthy feet. One common condition observed in individuals with diabetes is diabetic neuropathy. This refers to nerve damage that can cause loss of sensation in the feet, making it difficult to detect injuries like cuts, blisters, or sores. Without timely notice, these small injuries may develop into serious infections.
Circulation issues may also arise. These kinds of diseases occur when blood flow to the feet is reduced due to narrowed blood vessels. Reduced circulation delays healing, which makes even minor wounds more challenging to recover from, presenting elevated risks of complications. Recognizing these risks underscores the need for routine observation and dedicated care for foot health.
What Does Diabetic Foot Care Involve?
Diabetic foot care involves adopting regular precautions to keep feet healthy and minimize the likelihood of complications. By integrating consistent daily practices, individuals with diabetes can manage risks effectively. Some common aspects of foot care include:
- Daily Inspection: Examining the feet allows individuals to detect any abnormalities, like cuts, swelling, or redness.
- Gentle Cleaning and Moisturizing: Cleaning feet daily with warm, soapy water helps maintain hygiene. It is integral to dry the feet thoroughly afterward, especially between the toes, to prevent fungal infections.
- Nail Care: Trimming toenails straight across and gently filing any sharp edges can prevent ingrown nails. For individuals with limited dexterity or visibility, assistance from a professional may be valuable.
- Medical Supplies and Aids: Specialized insoles, orthotic footwear, or protective padding can provide additional support for individuals at greater risk of pressure-related injuries.
When Should You See a Podiatrist for Care?
Although regular self-care is beneficial, there are specific situations where consulting a podiatrist becomes advisable. Podiatrists are healthcare professionals who specialize in diagnosing and managing foot-related concerns. One scenario for seeking medical care includes identifying infections or wounds that do not show clear signs of healing.
Individuals experiencing significant numbness, tingling, or burning sensations in their feet may benefit from an assessment for diabetic neuropathy. Podiatrists may recommend strategies to mitigate the impact of neuropathy. Routine check-ups with a podiatrist can be valuable even without urgent concerns. These appointments allow specialists to monitor foot health regularly and address potential issues early.
Meeting With a Podiatrist
The integration of regular foot care with professional medical advice builds a holistic strategy for managing foot health with type 2 diabetes. By understanding how diabetes affects the feet, adopting daily care routines, and seeking guidance from healthcare professionals when needed, individuals can achieve a sustainable path to healthier outcomes. Whether you’re focusing on addressing specific issues or simply maintaining regular evaluations, expert input makes sure care remains comprehensive and personalized.




Leave a Reply